Over the last few years there has been an alarming surge in the number of side-channel attacks (SCAs). Security breaches are becoming increasingly common. Indeed, researchers recently revealed that they had been able to ‘jailbreak’ features and extract the encryption key of a well-known electric vehicle (EV) using a voltage glitch.
Companies—big and small—should be aware that hackers are finding new ways to exploit security vulnerabilities. It’s important to understand the range of applications that are at risk and what counter-measure solutions are available. This article focuses on voltage SCAs and offers examples of how an analog IP voltage glitch detector can help.
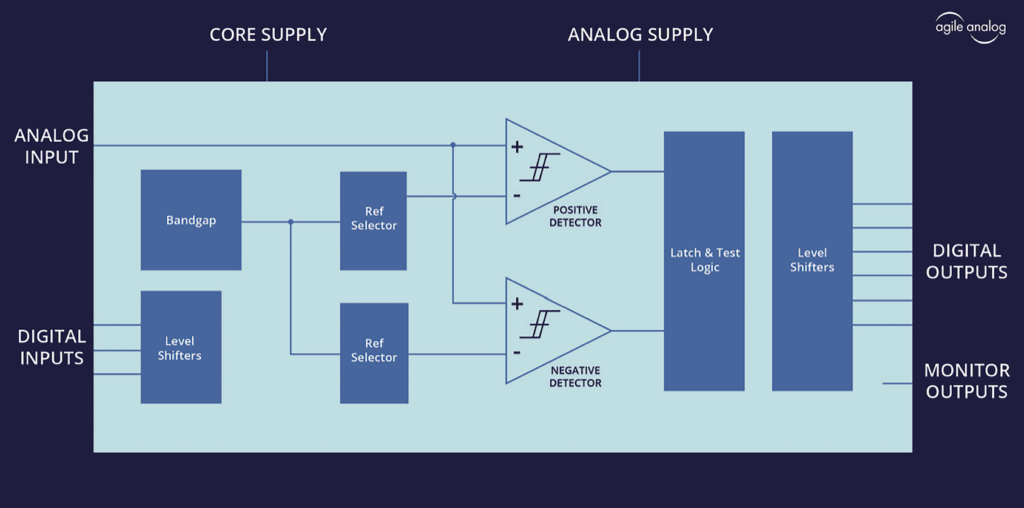
Agile Analog has created a voltage glitch detector IP called agileVGLITCH that can be incorporated into an SoC design. This configurable IP, along with Agile Analog’s temperature and clock attack monitor IPs, checks vital parameters like voltage, clock, and temperature for any changes that might point to an attack on the chip, such as supply voltage fluctuations or power supply manipulation. If these occur, the SoC’s processor is notified. Some example applications are as follows:
IoT Security Device: Consider a wireless door lock to a home, where a malicious person gains access to the lock and uses voltage glitching to enter the debug mode of the device, reading all the authorized keys for the lock. With agileVGLITCH embedded, the IoT security device can detect and record the voltage glitch, alerting the cloud system of an attack, and noting the date and time, which could help identify the culprit.
Security Camera: A security camera can be compromised using a voltage SCA to bypass the boot-signing sequence, allowing a malicious person to reset the system and then reflash unauthorized firmware. This would enable the hacker to view the video and audio stream content, which could be used for blackmail purposes. When using agileVGLITCH, the system can detect voltage glitch events and terminate any unauthorized activity.
Satellite TV: Consider the case where a hacker plans to remove digital rights management (DRM) from films broadcast over a satellite channel to resell the films. This can be achieved by installing a voltage glitcher on the HDMI controller supply to a satellite receiver with a valid subscription. By these means, the hacker can reset the HDMI output to be non-HDCP validated. Decrypted HD content can be streamed out to a non-secure device, which then re-encodes the content without protection. The agileVGLITCH IP can detect voltage glitching and prevent this from happening.
Automotive: An automotive supply regulator may have an undetected minor manufacturing flaw that causes a gradual increase in power supply resistance. When under heavy load, this could cause the voltage to fall below accepted safe levels. The agileVGLITCH sensor can identify voltage degradation that occurs over time. The system can relay this information back to the car manufacturer, which can identify vehicles that need correcting.
Conclusion
Side-channel attacks are increasing in frequency and severity. Companies must wake up to the fact that they need to take preventive action. Fortunately, there are advances in technology that can help to offer protection against a variety of different security vulnerabilities.

