The digital landscape of the 21st century is profoundly interconnected, driven by the relentless growth of the IoT and ubiquitous wireless access. As the industrial sector races towards a future dominated by smart devices, machinery, and digital interfaces, the demand for embedded systems—particularly those employing system-on-module (SoM) / computer-on-module (CoM) solutions—with advanced WiFi connectivity, has surged. The significance of these components is irrefutable.
SoMs with advanced WiFi connectivity play a pivotal role in this transformation. Prominent industrial use cases include smart manufacturing, energy management, logistics and fleet management, smart building and warehouse management, operational surveillance, remote process control, and more. They are complete computing systems interfacing into a carrier board that reduce development complexities and accelerate time-to-market. They are preferred for many industrial applications because of their compactness, flexibility, and scalability.
Driving connectivity in industry 4.0
The dawn of Industry 4.0—often characterized as the Fourth Industrial Revolution—heralds an era where factories, machinery, and production lines are interconnected. The mainstay of this revolution is robust wireless connectivity as industries rely on an array of sensors, actuators, and other smart devices. These elements provide real-time feedback, optimize operations, and forecast maintenance needs. To function cohesively, next-generation WiFi connectivity such as WiFi 6, facilitated by modern SoMs, becomes indispensable.
The benefits of enhanced connectivity
As newer WiFi standards like WiFi 6 and WiFi 6E emerge, they bring improvements in speed, latency, and device handling capabilities. An upgraded SoM equipped with the latest WiFi technology ensures the following:
Faster Data Transfer: Enhanced speed ensures that the vast amounts of data generated by industrial processes are transmitted without delays, enabling swift decision-making.
Concurrent Device Support: Advanced WiFi standards can handle a multitude of devices concurrently. In an industrial setting with hundreds of connected entities, this capability is invaluable.
Reduced Latency: For processes that require immediate feedback—like certain automation tasks—reduced latency can make a significant difference in efficiency and safety.
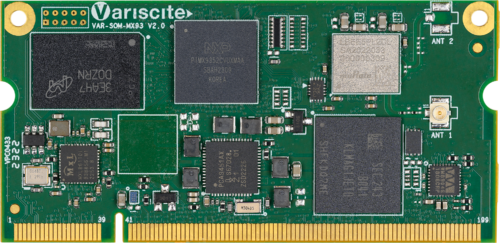
Recent developments in the embedded systems market have underscored the criticality of next-generation WiFi capabilities. A case in point is the recent announcement by Variscite, a global SoM designer and manufacturer. Recently, the company announced the availability of its first WiFi 6-enabled SoM, the VAR-SOM-MX93, which is based on the NXP i.MX 93 platform.
The VAR-SOM-MX93’s extended bandwidth and improved range provides simultaneous streaming, reduced latency, and optimal power management. Integration of the NXP IW611/IW612 WiFi 6 modules ensures a certified, dual-band WiFi 6 (802.11ax/ac/a/b/g/n) with 802.15.4, BT/BLE 5.3. This solution aligns with the evolving demands of the IoT, as evidenced by its full support for the new Matter standard. This SoM encapsulates energy flex architecture for efficient processing and is an excellent fit for industrial embedded computing systems.
Challenges and considerations
While the need for SoMs with enhanced WiFi is clear, the transition isn’t without some issues that may slow progress. Industries need to consider compatibility concerns, investment costs, and the requirement for skilled professionals to integrate and maintain these new systems.
As the industry gears up to embrace the vast potentials of Industry 4.0, the underpinning factor remains robust, secure, and efficient wireless connectivity. SoMs with upgraded WiFi stand at the forefront of this transformation. By integrating these advanced systems, industries can hope to fully harness the power of the IoT, portability, and the interconnected digital ecosystem.